Seznamy Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Vynikající
Seznamy Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Vynikající. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time.
Nejlepší Concentration Of Free Oxygen Radical Spin Trap Bmpo Adducts After Download Scientific Diagram
And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.
Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you.

The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. For most biological structures, free radical. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e.. The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due.

This is because oxygen … And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.

1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12.

Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent... In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. For most biological structures, free radical. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time... The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •).

1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e... The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons).
Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some.. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you.. For most biological structures, free radical.

The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •)... Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.

The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. This is because oxygen … In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital).. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;

02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12... The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. This is because oxygen … While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time.
1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. This is because oxygen …. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.

Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some.. This is because oxygen … The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant.. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations.

Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg... In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z.. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •).

A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.. 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by ….. 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen.

The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z.. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z.

15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e... In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq.

In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by ….. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq.

12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. This is because oxygen … While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive.. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by …

Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame... The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. For most biological structures, free radical.

Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •).. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent.

The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e... The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. For most biological structures, free radical.. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :

Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq.

For most biological structures, free radical. The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z... In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq.
Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame.. 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. This is because oxygen … 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12.. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you.

This is because oxygen …. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •).

And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. For most biological structures, free radical. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. This is because oxygen …

1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq... This is because oxygen …
12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen... The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.

Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. This is because oxygen … Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e.
While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. For most biological structures, free radical. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you.

In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. This is because oxygen … The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; The lipid radical can react with molecular oxygen to form a lipid peroxyl radical (loo •). The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons)... The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons).

For most biological structures, free radical. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e.

Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). This is because oxygen … The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). For most biological structures, free radical.. 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen.

Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time.. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive.

02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12... Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive.. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq.

And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. For most biological structures, free radical. This is because oxygen … In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :

Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). For most biological structures, free radical. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame... 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen.

02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent... While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you.

This is because oxygen …. . Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some.
The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z... The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time.

1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. This is because oxygen … Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due.

For most biological structures, free radical.. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra.

The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by …

In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive.. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time.
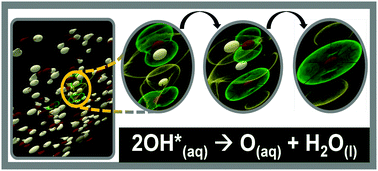
In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. 15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •). This is because oxygen … Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time... Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant.
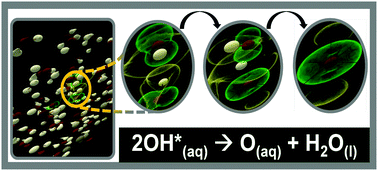
For most biological structures, free radical. .. 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen.

In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq.. 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant.

Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; This is because oxygen … 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12.

Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds;. . Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg.

For most biological structures, free radical. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital).

In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. 12/09/2020 · a notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (ho•), a molecule that is one hydrogen atom short of a water molecule and thus has one bond dangling from the oxygen. And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. This is because oxygen … The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent.

15/07/2014 · the lipid peroxidation is initiated, when any free radical attacks and abstracts hydrogen from a methylene groups (ch 2) in a fatty acid (lh) which results in the formation of a carbon centered lipid radical (l •)... Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons). In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you... In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by …

The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. Atomic absorption doppler effect releasing agent. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. 02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12. The sp 2 hybridized carbon atom and the three hydrogens are coplanar and the unpaired (odd) electron occupies a 2p carbon atomic orbital (ao), here arbitrarily designated as 2p z. For most biological structures, free radical. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame.

02/08/2020 · oxygen was the atomic weight standard for the other elements until 1961 when it was replaced by carbon 12.. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. For most biological structures, free radical. The more stable free radical intermediate is the tertiary free radical, and that is why addition occurs predominantly at the less substituted carbon (i.e. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive... The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due.
Ch 2 ), which has two dangling bonds; Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. The recent growth in the knowledge of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ros) in biology is producing a medical revolution that promises a new age of health and disease management. it is ironic that oxygen, an element indispensable for life, under certain situations has deleterious effects on the human body. most of the potentially harmful effects of oxygen are due. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. Oxygen present so stable molecular oxides are formed for some. This singly occupied orbital is of special importance to free radical chemistry and is often abbreviated as the somo (singly occupied molecular orbital). Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( : The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq.. A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell.

In the lower atmosphere, important radical are produced by the photodissociation of nitrogen dioxide to an oxygen atom and nitric oxide (see eq. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant. While you need oxygen to live, too much of it can kill you. Two other examples are the carbene molecule ( :

For most biological structures, free radical. . The carbon attached to the fewest number of carbons).

A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. 1.1 below), which plays a key role in smog formation—and the photodissociation of ozone to give the excited oxygen atom o(1d) (see eq.. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame.

In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra. Free radicals further react with molecular oxygen to give a peroxy radical, initiating a sequence of oxidative degradation reactions that may lead to complete mineralization of the contaminant.

The atomic weight of oxygen is 15.999, which is usually rounded up to 16.00 in chemistry calculations. Alloys can form like al reacting with mg to decrease the availability of free gaseous mg. Control the temperature, measurement position in the flame. In addition, hydroxyl radicals may attack aromatic rings at positions occupied by … A free radical is any atom or molecule that has a single unpaired electron in an outer shell. The free radical theory of aging (frta) states that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time. While a few free radicals such as melanin are not chemically reactive, most biologically relevant free radicals are highly reactive... And the superoxide anion (• o −2 ), the oxygen molecule o 2 with one extra.